CONNECTOR_GLUE_LINE
Connectors
"Optional title"
coid
entype${}_1$, enid${}_1$, entype${}_2$, enid${}_2$, pathid, $tol$, $\Delta$, $w$
$h$, $\rho$, $E$, $\nu$, $\sigma_f$, $\tau_f$, $G_I$, $G_{II}$
Parameter definition
Description
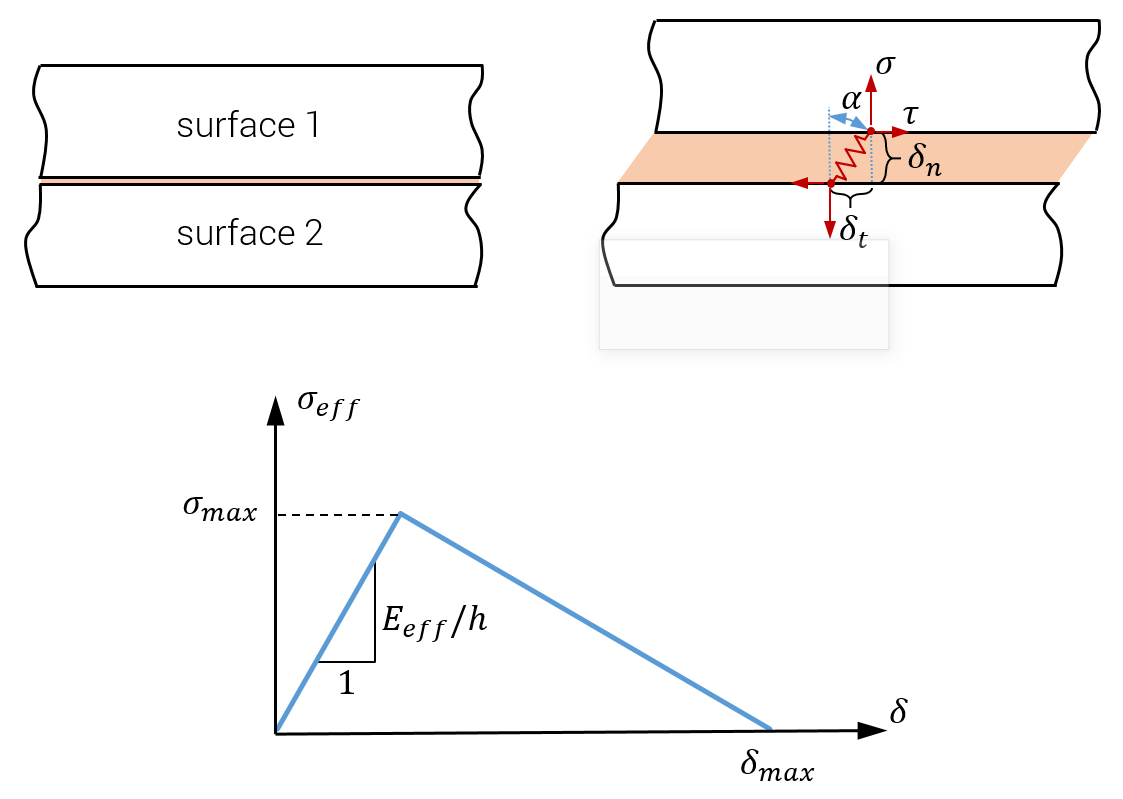
This command is used to define the effect of an adhesive between two surfaces. The location of the glue is defined with a PATH. The glue line is represented by a series of generalized spring elements with spatial spacing $\Delta$. The picture below shows stresses building up in one spring element. The shear stress $\tau$ is defined as:
$\displaystyle{ \tau = \frac{E}{2(1+\nu)} \cdot \frac{\delta_t}{h} }$
The normal stress component is:
$\displaystyle{ \sigma = \frac{(1-\nu)E}{(1+\nu)(1-2\nu)} \cdot \frac{\delta_n}{h} }$
A resultant (effective) stress measure in the spring is defined as:
$\displaystyle{ \sigma_{eff} = \sqrt{\sigma^2 + \tau^2} = \frac{E_{eff} \delta}{h} }$
where $E_{eff}$ is a direction dependent stiffness:
$\displaystyle{ E_{eff} = \sqrt{ \frac{(1-\nu)^2}{((1+\nu)(1-2\nu))^2} \cdot \mathrm{cos}^2 \alpha + \frac{1}{4(1+\nu)^2} \cdot \mathrm{sin}^2 \alpha } \cdot E }$
The definition of the loading angle $\alpha$ is shown in the figure below. $\sigma_f$ is the maximum stress in pure vertical loading and $\tau_f$ is the capacity in shear. The maximum effective stress $\sigma_{max}$ in a general direction of stretching is defined as:
$\displaystyle{ \sigma_{max}(\alpha) = \sigma_f \cdot \mathrm{cos}^2 \alpha + \tau_f \cdot \mathrm{sin}^2 \alpha }$
That is, damage will grow and the stresses will drop once $\sigma_{eff}$ reaches $\sigma_{max}$. We refer to the normal and shear stress components at this point as $\sigma_p$ and $\tau_p$, respectively.
$\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\sigma_p^2 + \tau_p^2} = \sigma_f \cdot \mathrm{cos}^2 \alpha + \tau_f \cdot \mathrm{sin}^2 \alpha}$
Also the work of fracture $G$ is direction dependent. The elongation at complete fracture $\delta_{max}$ is adjusted such that:
$\displaystyle{ G(\alpha) = \frac{1}{2} ( \sigma_p \cdot \mathrm{cos} \alpha + \tau_p \cdot \mathrm{sin} \alpha ) \delta_{max} = G_I \cdot \mathrm{cos}^2 \alpha + G_{II} \cdot \mathrm{sin}^2 \alpha}$
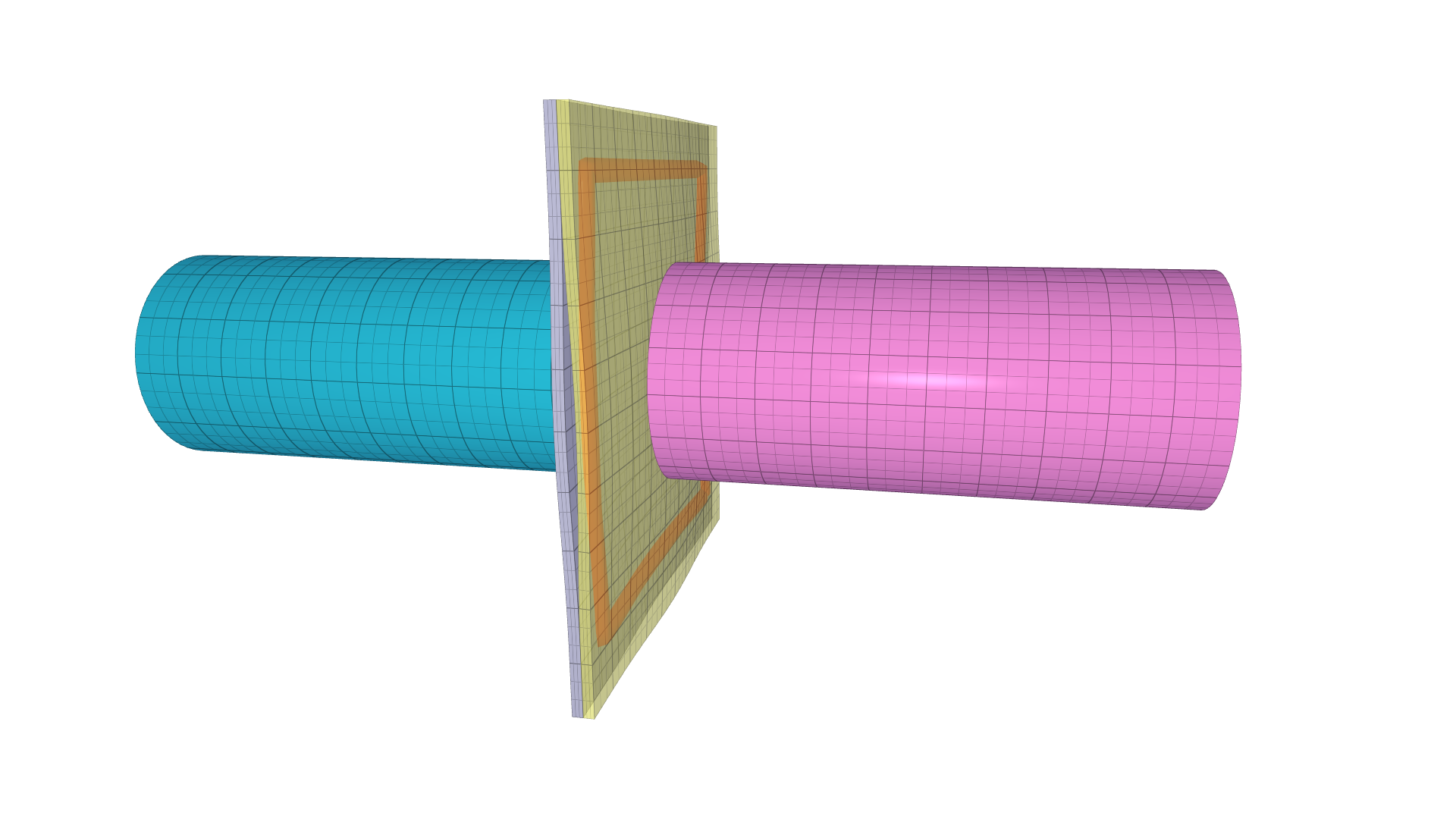
Example
Glued aluminum sheets exposed to tensile loading
A complete model of a glued connection exposed to tensile loading.