TRANSFORM_MESH_CYLINDRICAL
Mesh commands
"Optional title"
coid, entype, enid, csysid, fid${}_1$, fid${}_2$, fid${}_3$, fid${}_4$
Parameter definition
Description
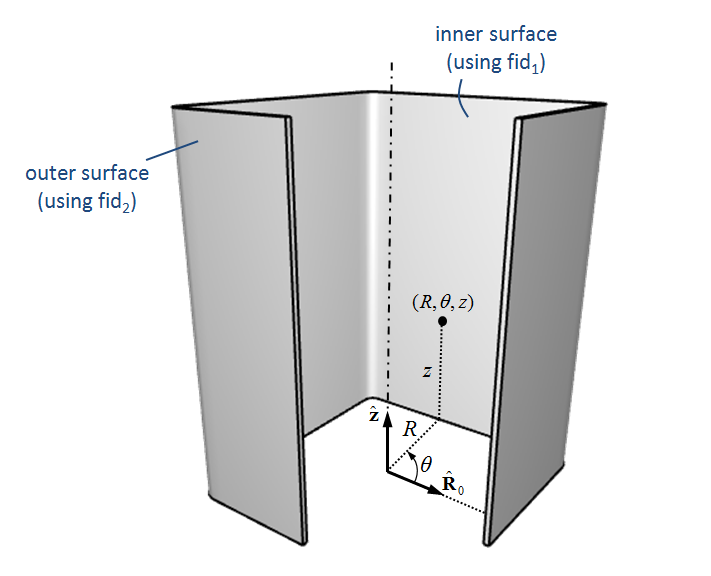
This command is used to transform a mesh. The transformation is expressed as diplacements in cylindrical coordinates $(R,\theta,z)$. $R$ is the radius, $z$ is the axial coordinate and $\theta$ is a circumferential angle ranging from $0^\circ$ to $360^\circ$.
If fid${}_1 \neq$ fid${}_2$ inner and outer surfaces use different radial transformations (see example below). In such situations only nodes on the surface of the body are transformed. Interior nodes are not treated. However, all nodes are transformed in the radial direction if fid${}_1 =$ fid${}_2$.
Example
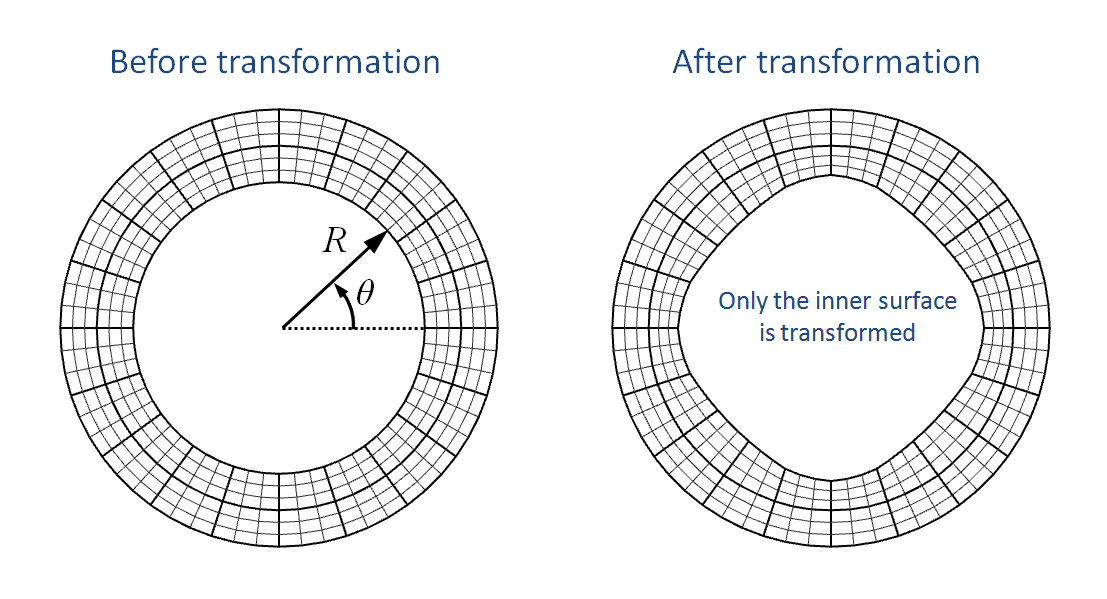
Transform mesh cylindrical - inner surface
Example where only the inner surface is transformed.
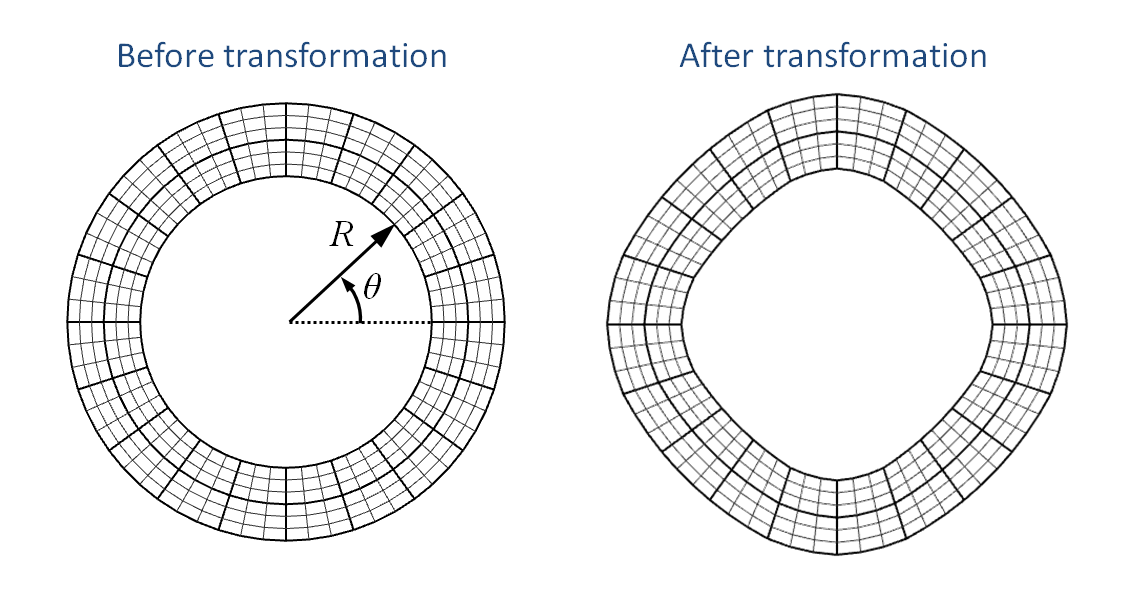
Transform mesh cylindrical - inner and outer surface
Example where the inner and outer surfaces are transformed using the same function. Note that also interior nodes are treated in this situation.
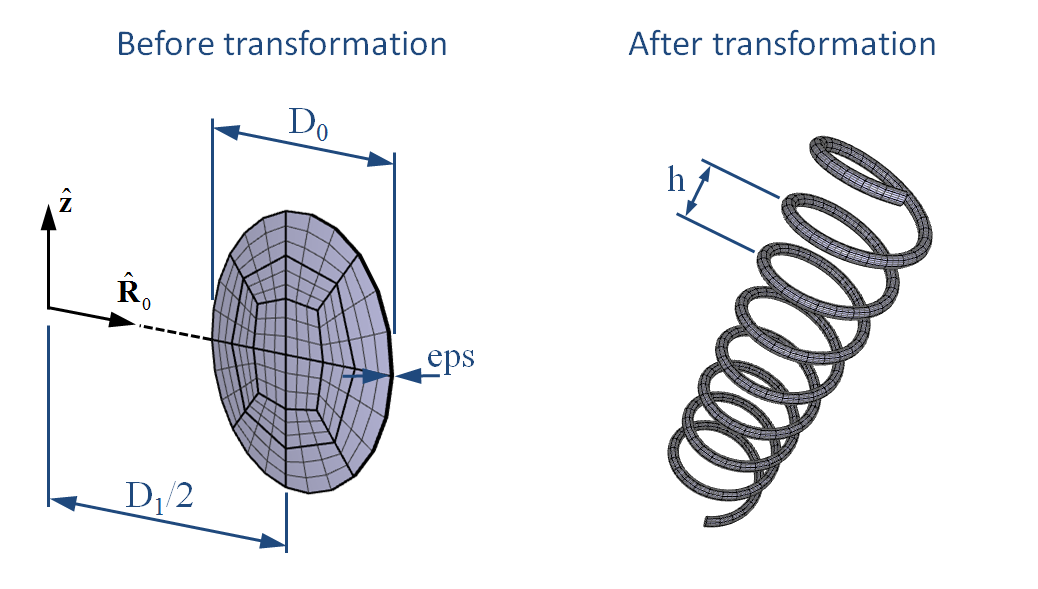
Transform mesh cylindrical - spring
Example using transformation displacements in axial and circumferential directions. A short cylinder is transformed into an object with the shape of a spring.